Code
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltStart by importing pytorch & matplotlib. I could not make the latex interpreter work in binder, so the corresponding lines are commented out.
The separability proprieties of several functions are investigated. This code first shows the separability proprieties of different ways of clustering the 1D space into two regions. Two types of functions are used to do so: * A sharp step function (Heaviside), * A smooth one (Tanh).
In both cases the position of the jump is parametrised by a scalar parameter \(\alpha\).
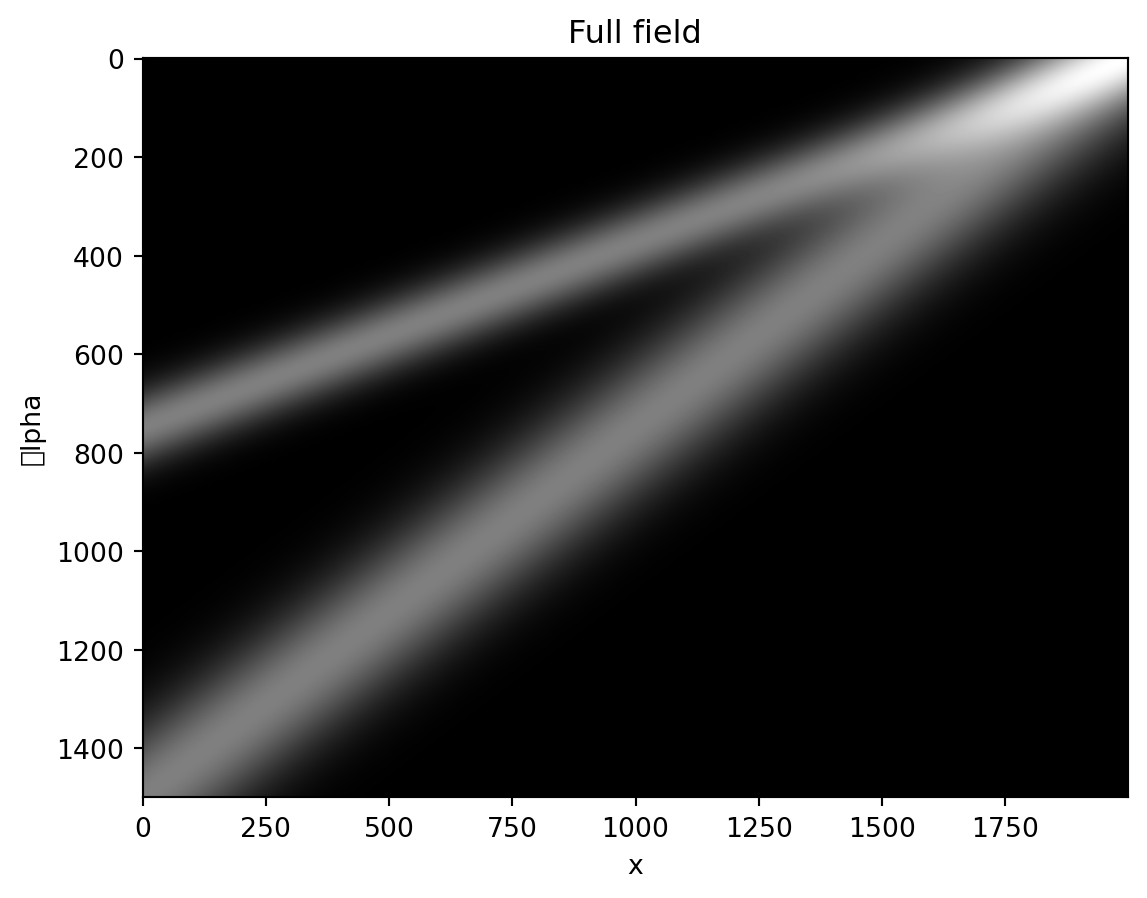
Furhter investigations are conducted on moving front(s) with a * A gaussian function that is moving * Two gaussian functions moving at different rates
L = 10 # Space domain
Alpha_vect = torch.linspace(0,1,1500) # vector of alphas
x_vect = torch.linspace(0,L,2000) # vector of x
Function = 'Heaviside' # Alpha-parameterised step function
Function = 'Tanh' # smooth alpha-parameterised step function
# Function = 'Gauss' # Alpha-parameterised front function
Function = 'Gauss_sum' # Double alpha-parameterised front functions
if Function == 'Heaviside':
F = torch.heaviside((x_vect[:,None] - (1-Alpha_vect[None,:])*L), x_vect[-1]/x_vect[-1])
elif Function == 'Tanh':
F = torch.tanh((x_vect[:,None] - (1-Alpha_vect[None,:])*L))
elif Function == 'Gauss':
F = torch.exp(-(x_vect[:,None] - (1-Alpha_vect[None,:])*L)**2)
elif Function == 'Gauss_sum':
F = torch.exp(-(x_vect[:,None] - (1-Alpha_vect[None,:])*L)**2) + torch.exp(-(x_vect[:,None] - (1-2*Alpha_vect[None,:])*L)**2) /Users/daby/anaconda3/lib/python3.11/site-packages/IPython/core/pylabtools.py:152: UserWarning:
Glyph 7 () missing from current font.
The truncated function and its reference are compared for two values * \(\alpha = 1/3\) & * \(\alpha = 2/3\).
plt.plot(x_vect,F[:,1000],'k',label='Full, alpha = 2/3')
plt.plot(x_vect,F_truncated[:,1000],'--',label='Truncated, alpha = 2/3')
plt.plot(x_vect,F[:,500],'k',label='Full, alpha = 1/3')
plt.plot(x_vect,F_truncated[:,500],'--',label='Truncated, alpha = 1/3')
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.title(f'2 slices of the field, N={N}')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x,alpha)')
# plt.savefig(f'../Results/Sliced_TruncatedField_{N}_'+Function+'.pdf', transparent=True)
plt.show()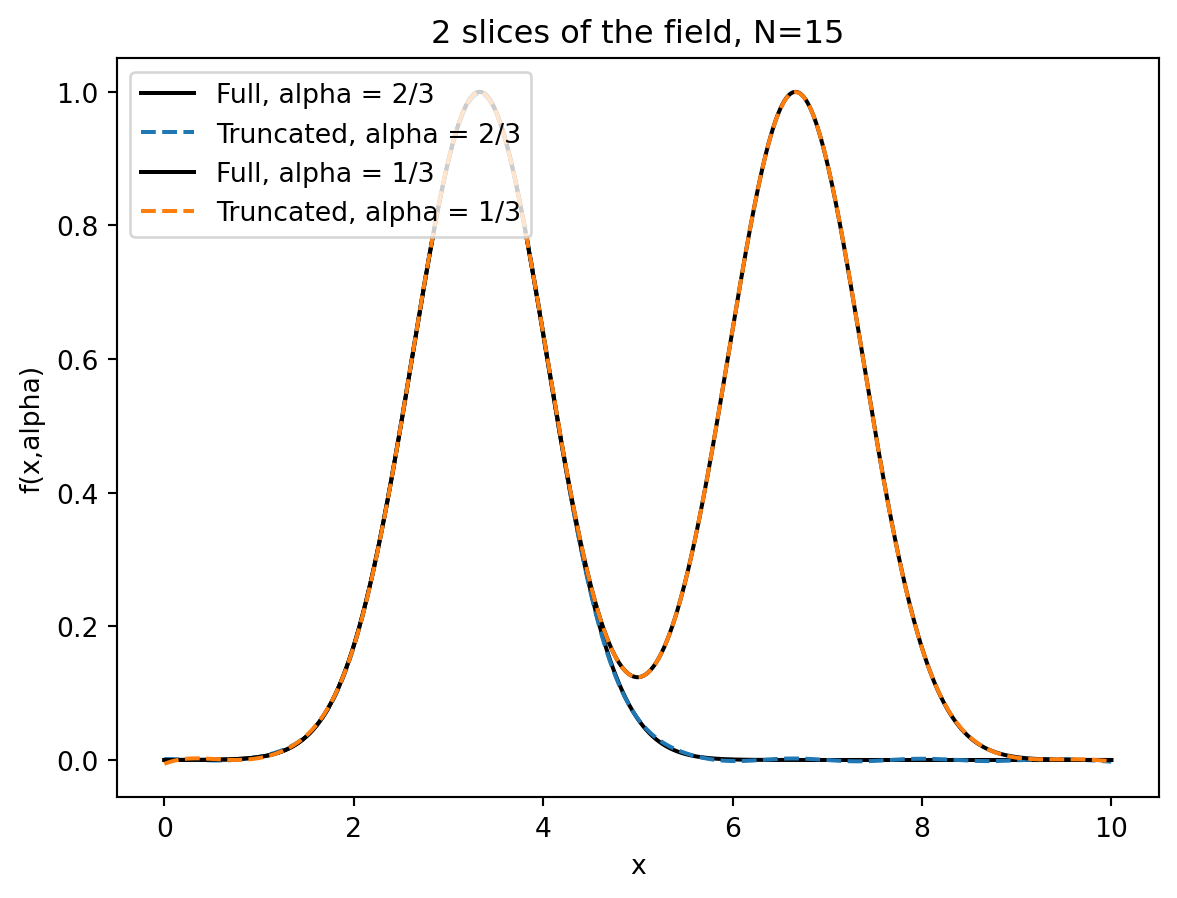
This interactive plot allows to change the number of modes in the truncation and the value of the parameter \(\alpha\) .